Comparing Futures & Margin Trading: The Differences in Crypto Margin vs Futures Trade
2024-01-15 09:09:35Understanding Leverage in Cryptocurrency Trading
In the dynamic world of cryptocurrency trading, leverage stands as a powerful tool, offering traders the ability to amplify their market positions beyond their immediate capital. This concept, while lucrative, introduces a heightened level of risk and complexity, necessitating a deep understanding for successful navigation. Leverage in cryptocurrency trading enables investors to increase their exposure to market movements without requiring the full capital normally needed for such positions.
What Is Leverage?
Leverage in the context of cryptocurrency trading is essentially borrowing capital to increase potential returns on investment. It allows traders to open larger positions than their own capital would permit by using borrowed funds from a broker or exchange. For instance, with leverage of 10:1, a trader can control a position worth ten times their own investment. This means that even small movements in the market can lead to substantial profits or losses, proportionate to the leveraged amount. Leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 10X, 50X, or even higher, indicating the extent to which the investment is multiplied.
Importance of Leverage in Margin and Futures Trading
In margin and futures trading, leverage plays a critical role. Margin trading involves borrowing funds to trade assets, where these assets serve as collateral for the loan. Here, leverage magnifies both profits and losses, making it a double-edged sword. In futures trading, leverage is inherently built into the product, as traders are required to put up only a fraction of the contract’s total value, known as the margin. This leverage allows for significant exposure to the cryptocurrency markets with a smaller upfront investment. However, it's crucial for traders to understand the risks involved, as leverage can also amplify losses, leading to margin calls or the liquidation of positions if the market moves unfavorably.
Exploring the Basics: What is Margin Trade?
Margin trading is a method where traders speculate on the price movements of an asset, such as cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, by using borrowed funds. It differs from spot trading as it involves leveraging borrowed money to maximize potential gains from an asset's price changes. This approach amplifies potential returns but also increases the potential for significant losses, making it a double-edged sword. The basic operating principle of margin trading is the use of borrowed funds to increase market exposure beyond what would be possible with one's own capital. This strategy hinges on the belief that the returns from the investment will exceed the cost of the borrowed funds.
Margin Account: A Key Player in Margin Trade
The margin account is an indispensable component in margin trading. Unlike a standard trading account, a margin account allows investors to borrow money from a broker, using their own investment as collateral. The process starts with the trader setting up a margin account, distinct from a regular spot account, which allows them to borrow funds. This borrowing amplifies their exposure to the crypto market, a concept known as leverage. The borrowed funds accrue interest, which is paid to the lenders based on market rates.
On the FameEX platform, you might need to activate your Margin Trading account first, and then you can start using the Borrow feature. Currently, there is only 5x leverage available for BTC and ETH pairs. You should transfer your funds to the Margin Wallet first. Then, use the Borrow feature to borrow funds to buy cryptocurrencies.
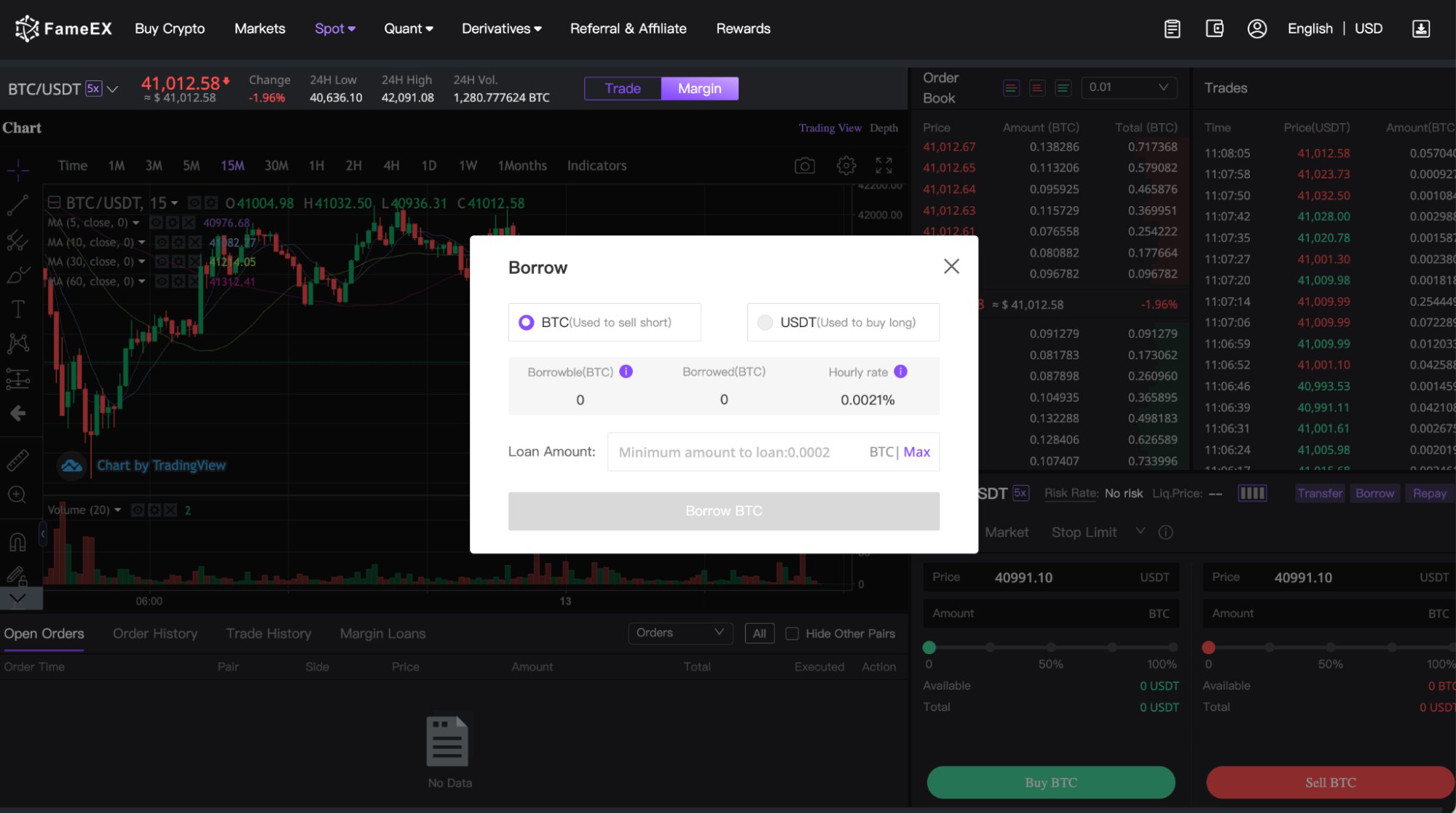
Risks and Benefits of Margin Trading
Margin trading comes with its set of risks and benefits, making it a compelling yet cautious strategy for traders. On the benefits side, margin trading can significantly amplify profits. Since traders can control a larger amount of securities than their capital alone would allow, the potential for higher returns increases correspondingly. However, the risks are equally amplified. Losses can exceed the initial investment, and in rapidly declining markets, traders may face margin calls, requiring them to provide additional funds to repay their borrow. Additionally, the costs of borrowing funds can sometimes outweigh the gains from investments, particularly in markets with low volatility or negative trends. As such, margin trading requires a clear understanding of market dynamics, robust risk management strategies, and a disciplined approach to trading.
Delving into Details: What is Futures Trade?
Futures trade, a cornerstone of the financial derivatives market, involves the agreement to buy or sell an asset without a predetermined future date and price. Futures trading shares similarities with margin trading, but there are distinct differences. In futures trading, participants engage in buying or selling contracts that reflect the value of a specific cryptocurrency. This approach contrasts with margin trading, where the underlying cryptocurrency is not directly owned by the trader. Similar to margin trading, futures contracts enable investors to leverage considerable capital, providing a means to safeguard their investment portfolio. This hedging strategy allows traders to maintain their cryptocurrency assets without having to sell them at a loss.
Risks and Benefits of Futures Trading
Cryptocurrency futures contracts are commonly employed as a strategy to mitigate the risk associated with the volatility and potential adverse price movements of the underlying asset. Futures trading offers a blend of risks and benefits, making it an attractive but nuanced strategy for investors. One of the primary benefits is the ability to hedge against price volatility. This characteristic enables futures traders to potentially profit even during market downturns, capitalizing on the fluctuations in price regardless of the overall market trend. By securing a future price for an asset, investors can manage their exposure to price fluctuations, providing a measure of financial stability. Futures also provide opportunities for speculative gains, as traders can profit from the differences in the contract price and the market price at settlement. However, the risks are significant. The leverage involved in futures trading can lead to large losses, particularly if the market moves unfavorably. Additionally, since futures contracts are binding, investors face the risk of having to fulfill contracts at a loss. The potential for rapid market changes requires traders to be vigilant and well-informed about market trends and risks.
Futures Contract: A Vital Component in Futures Trade
The futures contract is the fundamental unit in futures trading. It is a legally binding agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future date and price. These contracts detail the quantity and quality of the underlying asset, the specific price per unit, and the date of settlement. Futures contracts are standardized and traded on futures exchanges, which facilitate the buying and selling process and provide a degree of security and regulation. A key feature of these contracts is their tradability before the settlement date, allowing investors to exit positions or realize profits/losses prior to the contract's conclusion. The standardized nature of futures contracts ensures liquidity and enables investors to make precise calculations regarding their exposure and potential returns.
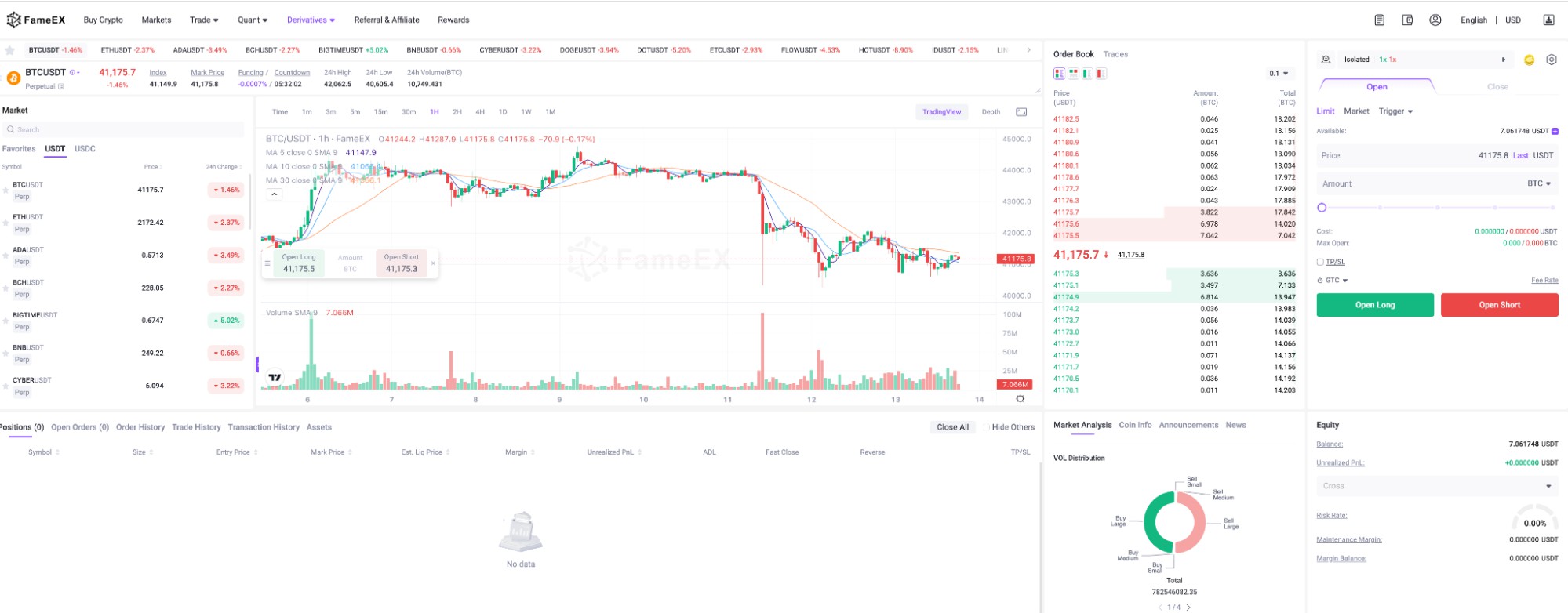
Comparing Margin and Futures Trading
When it comes to advanced trading strategies, margin and futures trading are prominent methods used by investors to leverage their positions and potentially amplify returns. Although both approaches involve the use of leverage and are popular in the realm of derivatives trading, they are founded on different principles and serve distinct purposes.
Key Differences Between Margin and Futures Trading
Understanding the similarities and differences between margin and futures trading is crucial for traders to make informed decisions, optimize their trading strategies, and manage risks effectively. This comparison delves into their core characteristics, highlighting how each method operates and the unique aspects they bring to the trading table.
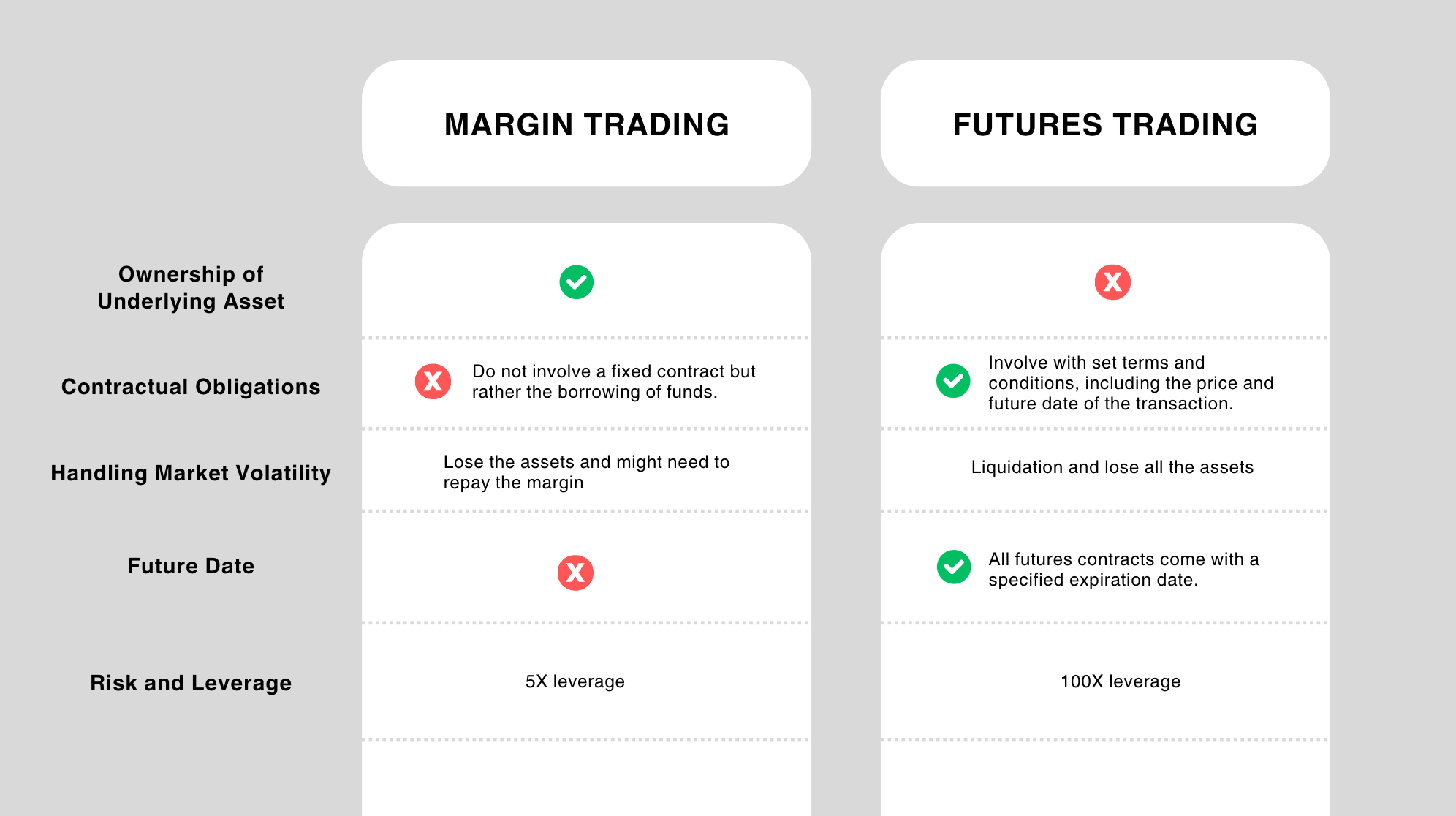
.Ownership of Underlying Asset
In futures trading, traders are required to provide a collateral deposit, often referred to as a good faith deposit in order to mitigate risk. Conversely, in the cryptocurrency market, margin accounts enable traders to leverage their positions in the spot market through the use of borrowed funds. This form of leverage constitutes a loan, upon which interest must be accrued and paid, thus introducing an additional financial consideration for traders in the cryptocurrency domain.
.Contractual Obligations
Futures trading involves entering into a standardized smart contract with set terms and conditions, including the price and future date of the transaction. Margin trading, on the other hand, does not involve a fixed contract but rather the borrowing of funds to engage in larger trades, with the obligation primarily being to repay the borrowed funds plus any interest or fees.
.The Initiating Process: Initial Margin vs Futures Contract
The initiation of a margin trade requires the trader to deposit an initial fund, which is a percentage of the total trade value and serves as collateral. In margin trading, traders borrow funds to buy assets, and this borrowing and purchasing process constitutes both a transaction and an investment. Subsequently, traders are obliged to repay the borrowed assets. However, in futures trading, initiation involves entering into a futures contract. This contract specifies the terms of the future transaction, including the price and date of settlement. Liquidation in this context only occurs with the total investment involved.
.Handling Market Volatility: Margin Call vs Perpetual Futures
In margin trading, a margin call occurs when the value of an investor's account falls below the broker's required level. This situation necessitates the investor to either provide additional funds or sell assets. Perpetual futures, commonly utilized in cryptocurrency markets, are futures contracts without an expiry date. These contracts offer a method to speculate on price movements and manage risks associated with market volatility differently from traditional futures. In the volatile crypto market, margin trading may lead to situations where the borrowed assets are insufficient to cover losses, prompting traders to infuse additional funds to offset these losses. All futures contracts come with a specified expiration date. Conversely, in perpetual futures, market volatility may lead to liquidation, resulting in traders losing all their assets. However, unlike margin trading, they are not required to contribute additional funds. Both margin trading and perpetual futures represent distinct trading strategies for market participants to manage risks.
.Determining the Future: Future Date in Margin vs Date in Futures
In margin trading, there is no predetermined future date for the settlement of transactions, which offers flexibility but also introduces unpredictability in holding periods. Perpetual futures contracts do not have a fixed settlement date, providing additional flexibility and more choices in futures trading. However, in futures trading, there is an 8-hour funding rate that each counterpart must pay, which may incur additional fees.
.Risk and Leverage
Both margin and futures trading involve high levels of risk and leverage, which can amplify both gains and losses. However, the nature and management of risk differ. Margin trading exposes traders to the risk of margin calls and potential liquidation with 5X leverages now on FameEX, while futures trading involves the risk related to contract obligations and market movements, which are predetermined by the contract terms. Both investments involved risks and leverages with margin trading only with 5X, however, in futures contracts, users can use up to 100X leverage to amplify the profits.
Similarities Between Margin and Futures Trading
Despite their differences, margin and futures trading share several key similarities that attract investors looking to leverage their trades and potentially increase their returns:
・Use of Leverage:
Both strategies allow traders to control a larger position than what their capital would normally permit. Leverage enables traders to amplify their exposure to market movements, thereby increasing the potential for higher profits, but also for greater losses.
・Potential for High Returns and High Risks:
Due to the leverage involved, both margin and futures trading offer the possibility of significant returns on a relatively small investment. However, this also means that losses can be equally magnified, potentially exceeding the initial investment.
・Market Speculation:
Both methods are commonly used for speculation, where traders attempt to predict market movements to make profits. This involves making educated guesses about future price movements of assets, without necessarily having a long-term investment interest in them.
・Sophisticated Trading Strategies for Experienced Traders:
Both margin and futures trading are considered more advanced trading strategies. They are typically more suitable for experienced traders who have a deeper understanding of the markets and the risks involved.
・Short Selling Capability:
Both strategies allow for short selling, where traders can profit from declining asset prices. This involves selling borrowed assets (in margin trading) or selling futures contracts, with the intention of buying them back at a lower price.
・Market Accessibility and Liquidity:
Both margin and futures trading provides traders with greater market accessibility and the potential for increased liquidity. This is especially useful for traders looking to enter or exit positions quickly in response to market movements.
Detailed Analysis: Margin Trading vs. Futures Trading
Margin trading and futures trading stand out as two pivotal strategies employed by traders to maximize their market influence and potential profits. While both techniques involve the use of leverage and are integral to modern financial markets, they operate under different mechanisms and cater to varied trading objectives. This detailed analysis seeks to dissect and compare margin trading and futures trading, offering a comprehensive understanding of their functionalities, risk profiles, and suitability for different market scenarios. By delving into these strategies, traders can better navigate the complexities of each approach and make informed decisions that align with their investment goals and risk appetite.
Impact of Market Conditions on Margin and Futures Trading
Market conditions play a significant role in shaping the outcomes of both margin and futures trading, each responding differently to market dynamics:
- Volatility Impact: In highly volatile markets, margin trading can be particularly risky due to the potential for frequent margin calls and rapid changes in account equity. Futures trading, while also affected by volatility, offers more predictability due to the predefined nature of futures contracts.
- Market Trends: Bullish or bearish trends can influence the strategies used in both types of trading. In a bullish market, margin traders might be more inclined to borrow and invest more heavily, whereas, in futures trading, long positions may be favored. Conversely, in bearish markets, short selling becomes more prevalent in margin trading, and short futures contracts may be more common.
- Interest Rates and Dividends: Changes in interest rates can affect the cost of borrowing in margin trading, thereby impacting profitability. For futures trading, interest rates can influence the pricing of contracts, especially for financial futures.
Consideration of Liquidity and Position Entry/Exit in Margin vs Futures Trading
Liquidity and the ease of entering or exiting positions are critical considerations in both margin and futures trading, yet they manifest differently in each:
- Liquidity Considerations: Futures markets are generally highly liquid, especially for major contracts, facilitating easier entry and exit of positions. Margin trading liquidity is more dependent on the underlying asset being traded and the market conditions at the time.
- Position Entry and Exit: Entering and exiting positions in margin trading can be more straightforward, as it typically involves buying or selling the underlying asset directly. In futures trading, entering a position means engaging in a contract that might require holding until expiration or actively managing the position to exit before expiry.
- Cost Implications: The costs associated with entering and exiting positions can vary. In margin trading, the primary costs are interest on borrowed funds and trading fees. In futures trading, costs include trading fees, funding rate and, potentially, the spread between bid and ask prices.
Implementation of Both Margin and Futures Trading in Investing
The implementation of margin and futures trading stands as a testament to the evolving sophistication and strategic depth of modern financial markets. These two methods, each with its own set of rules and potential rewards, offer investors diverse avenues to amplify their market positions, hedge risks, and capitalize on market movements. Understanding how to effectively incorporate both margin and futures trading into an investment strategy can significantly enhance an investor's ability to navigate various market conditions and achieve their financial objectives. This discussion focuses on the strategic integration of these tools into an investor's portfolio, highlighting the nuances, potential synergies, and considerations that come with employing margin and futures trading in concert.
Strategies for Using Margin and Futures Trading for Improved Investing
Effectively balancing risk and reward is crucial. Margin trading offers investors the opportunity to leverage their positions in markets where they have strong confidence. This approach amplifies the potential for significant gains, but also increases risk exposure. To counterbalance this, futures trading can be strategically employed as a hedge against potential losses in these leveraged positions. This dual strategy not only mitigates risks but also paves the way for capital growth. By leveraging positions through margin trading while simultaneously using futures for hedging, investors can maneuver through the complexities of the market with a well-rounded approach that seeks to maximize rewards while keeping risks in check.

Further enhancing this strategy is the diversification of the investment portfolio. By integrating both margin and futures trading, investors can spread their investments across a variety of asset classes and markets. Futures trading opens the door to a range of assets including different cryptocurrencies investment opportunities. Conversely, margin trading is typically utilized for few crypto choices in investments such as BTC/USDT or ETH/USDT on FameEX platform. This blend of strategies not only diversifies the portfolio but also provides a balanced mix of short-term and long-term investment tactics. Margin trading is ideal for short-term, tactical market moves, while futures contracts are more suited for longer-term strategies and robust hedging against market volatility. This combination of margin and futures trading promotes capital efficiency, enabling investors to maximize their investment potential with less capital upfront, and offering substantial market exposure through a relatively small initial investment in futures.
Case Study Illustrating the Use of Both Margin and Futures in Investing
Consider an investor who has a bullish outlook on a technology stock but is concerned about short-term market volatility. The investor could use margin trading to purchase cryptocurrencies, leveraging their position for greater exposure. Simultaneously, they could use futures contracts to buy put options on the same cryptocurrencies. This strategy would allow the investor to benefit from any upside in the stock while the futures contract would provide a hedge against significant downside risk.
Another example is an investor with a diversified portfolio of cryptocurrencies. To protect against a potential market downturn, they could use futures contracts to short a crypto market, providing a hedge against their holdings. If the market does decline, the gains from the futures contract could offset some of the losses in their margin account from the declining prices. These case studies demonstrate how margin and futures trading can be strategically used together to create a more robust and flexible investment approach, leveraging opportunities while managing risks.
How do Trading Platforms Facilitate Margin and Futures Trade?
In the contemporary landscape of financial markets, trading platforms play a pivotal role in facilitating margin and futures trade, offering investors an accessible and efficient gateway to these sophisticated trading strategies. These platforms, ranging from traditional brokerage firms to cutting-edge crypto exchanges like FameEX, provide the necessary tools, resources, and infrastructure needed for executing margin and futures transactions. By bridging the gap between individual traders and global financial markets, these platforms have democratized access to advanced trading techniques, making them available to a wider audience than ever before.
Role of Trading Platforms in Margin and Futures Trade
Trading platforms play a pivotal role in the realm of margin and futures trading, offering several essential functions to facilitate effective trading activities. A primary feature of these platforms is the provision of access to leverage, a key element in both margin and futures trading. These platforms establish the parameters for leverage use, including setting limits and requirements. This aspect is critical as it enables traders to amplify their trading positions beyond their actual capital, thus potentially increasing both the profits and risks. Additionally, trading platforms are instrumental in providing market connectivity and execution. They link traders to an extensive range of financial markets and furnish real-time data, which is vital for timely and efficient trade execution. This feature is particularly crucial in the fast-paced trading environment of margin and futures markets, where price fluctuations are rapid and significant.
Furthermore, trading platforms are equipped with advanced risk management tools to assist traders in navigating the volatile market landscape. These tools include the implementation of stop-loss orders, margin calls, and real-time account monitoring, all of which contribute to a more effective management of risks associated with high-leverage trading. Alongside these technical features, many platforms also offer educational resources and support. They provide traders with instructional materials, tutorials, and customer service, aimed at enhancing their understanding of the intricacies of margin and futures trading. This educational aspect is vital for enabling traders to make informed decisions and develop robust trading strategies. Trading platforms are integral to the margin and futures trading ecosystem, offering tools and resources that support traders in managing risks, executing trades efficiently, and making informed decisions in a complex and fast-moving financial environment.
Different Trading Offers by Crypto Exchanges
Crypto exchanges have significantly expanded their trading offerings, tailoring them to meet a broad spectrum of investor requirements. One fundamental type of trade is Spot Trading, which represents the conventional practice of buying and selling cryptocurrencies for immediate settlement. This straightforward approach is most common among investors seeking to trade digital assets in real time. Additionally, crypto exchanges have embraced Margin Trading, a more sophisticated strategy that allows traders to borrow funds, thereby amplifying their buying power. This method is especially appealing to those looking to leverage their investments for potentially higher returns, albeit with a higher risk.
Further diversifying their services, crypto exchanges now offer Perpetual Futures Trading, enabling traders to engage in contracts that speculate on the future prices of various cryptocurrencies. This approach allows investors to bet on price movements without the need to own the actual cryptocurrencies. At FameEX, they offer two types of futures trial funds for users to experience futures trading without using their own assets. This is a great opportunity for beginners to join and gain a new perspective on what futures trading is all about.
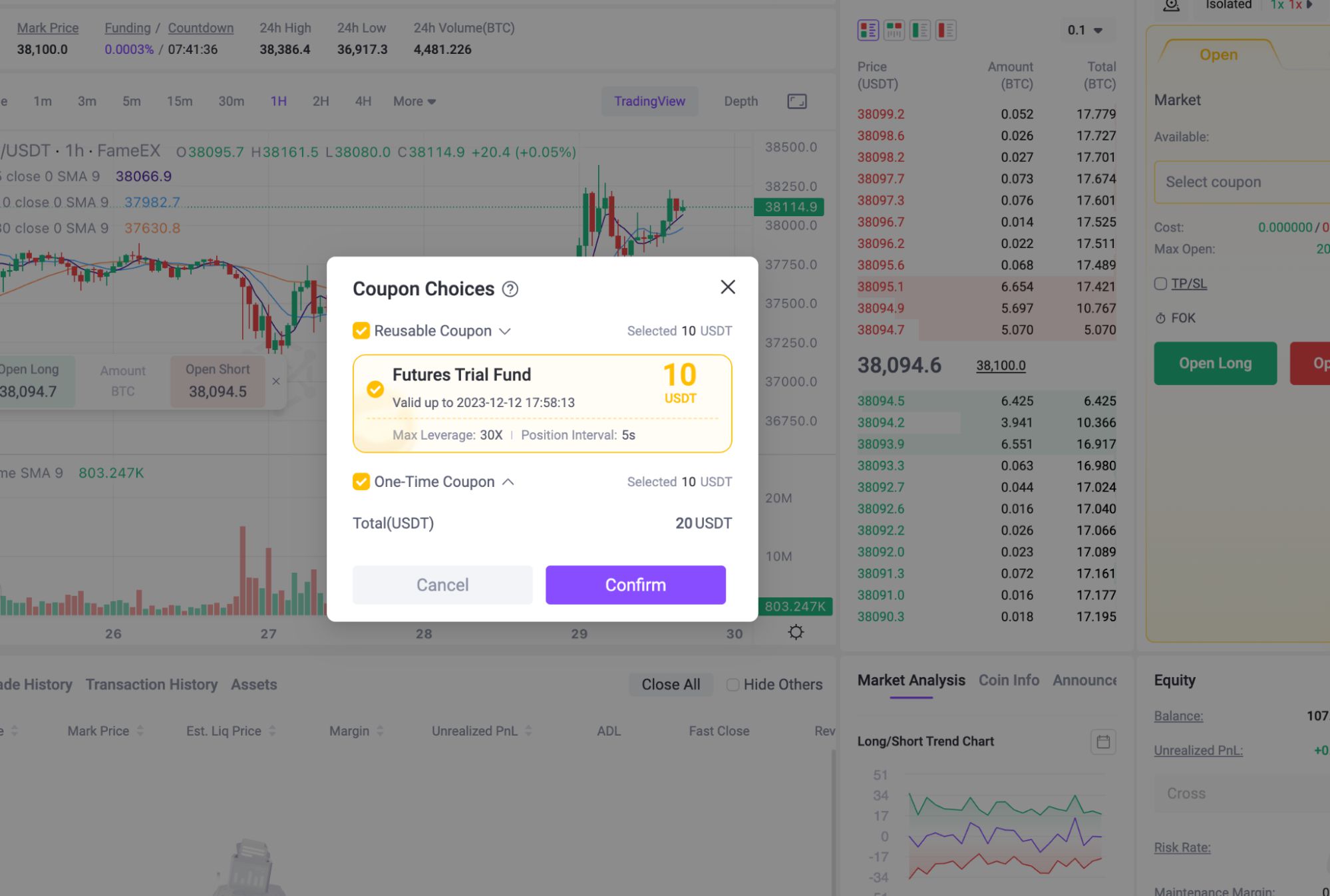
Alongside this, some exchanges have ventured into Options and Derivatives. These financial instruments also provide traders with an array of advanced tools for both hedging and speculative strategies. By incorporating these various trading options, crypto exchanges have evolved into comprehensive platforms that cater to the diverse strategies and risk appetites of modern cryptocurrency investors.
The Benefits Associated with Margin & Futures Trading on Platforms
Trading platforms have emerged as pivotal facilitators in both margin and futures trading, offering an array of benefits that cater to both new and experienced investors. One of the primary advantages is accessibility; these platforms simplify advanced trading strategies, making them more approachable to a wider audience. They also excel in providing convenience and efficiency. This is largely due to their user-friendly interfaces, mobile application availability, and integration of various trading tools, which collectively streamline the trading process. Furthermore, these platforms create avenues for diversification, allowing traders to broaden their investment strategies across a diverse range of assets and products.
Additionally, these platforms are at the forefront of incorporating advanced technology and analytics into trading. They offer sophisticated charting tools, calculators, detailed analytics, and automated trading systems, which significantly aid traders in making informed decisions and implementing effective strategies. Reputable trading platforms strictly adhere to regulatory standards, ensuring a secure trading environment and safeguarding traders’ investments. In essence, trading platforms have become indispensable in the margin and futures trading ecosystem. They provide comprehensive services and tools that not only enhance the overall trading experience but also manage risks effectively and open up opportunities for diversified investment strategies.
Should You Opt for Margin or Futures Trading?
Choosing between margin and futures trading is a crucial decision that hinges on an investor's goals, risk tolerance, and trading strategy. This decision is not just about selecting a financial instrument; it's about aligning your investment approach with your personal financial objectives and comfort with risk. As you delve into this exploration, consider how each option fits within the broader context of your financial portfolio. Margin trading offers lower leverage, while futures trading provides a structured approach to speculate or hedge on future prices of assets. Understanding the nuances and implications of each will guide you towards a decision that complements your investment style and risk profile. This discussion aims to encourage readers to thoughtfully assess whether margin or futures trading aligns with their trading objectives and risk capacity.
For example, in margin trading, you should consider whether you have the ability to repay the funds if you lose all or part of them. On the other hand, in futures trading, you need to assess if you are prepared to accept the possibility of losing your entire investment due to liquidation. These considerations should be taken into account before deciding on which investment strategies to pursue.
Margin Vs Futures: What Suits You the Best?
In the realm of financial trading, choosing the right strategy on margin or futures trading hinges on individual trading objectives and risk tolerance. Margin trading is a prime choice for traders seeking short-term gains in the stock market. This approach leverages the trader's capital, enabling them to potentially amplify returns. However, it demands a nuanced understanding of crypto market dynamics. It allows traders to speculate on future prices or serves as a hedge against other investments. Futures trading requires insight into broader market trends, including global economic indicators, making it suitable for those who comprehend these complex factors.
The risk profile of each trading type is also a crucial consideration. Margin trading introduces the risk of margin calls and the possibility of losses exceeding the initial investment. This high-stakes environment necessitates careful risk management and constant market vigilance. On the other hand, futures trading, while still involving risks, provides a more structured risk environment. The risks are bound within the terms of the futures contract, offering a more predictable framework for risk management. Therefore, choosing between margin and futures trading depends largely on an individual’s risk appetite, market knowledge, and specific financial goals.
Evaluating Risks: Associated with Margin and Futures Trading
It's essential to comprehend the inherent risks, particularly those stemming from the use of leverage. Leverage, a common feature in both strategies, allows traders to control large positions with a relatively small amount of capital. This can result in substantial gains when the market moves favorably; however, it also poses a significant risk as it can equally amplify losses. The degree of leverage used and its potential repercussions should be a primary focus for any trader in these markets. A deep understanding of how leverage works and its impact on investment returns is crucial for effective risk management in both margin and futures trading.
Additionally, the influence of market volatility and liquidity issues cannot be understated. In margin trading, rapid price fluctuations can lead to margin calls, where traders are required to provide additional funds to maintain their positions. This necessitates a vigilant approach to market trends and potential price shifts. Futures trading, on the other hand, involves navigating the swings in contract values that arise from market volatility. The impact of these swings can be significant, given the nature of futures contracts. Liquidity is another pivotal factor in both margin and futures markets. The ease of entering and exiting positions depends heavily on the liquidity of the traded asset. A lack of liquidity can lead to challenges in executing trades at desired prices, thereby affecting the overall trading strategy and risk exposure. Hence, traders must be acutely aware of the liquidity levels in their chosen markets and how these can affect their trading decisions.
Financial Perspective: Margin or Futures?
Both margin and futures trading offer unique opportunities and requirements that cater to different investment strategies. Margin trading is particularly notable for its lower initial capital requirements when compared to purchasing assets outright. This method allows traders to borrow funds to buy cryptos, thereby leveraging their investment. However, it comes with the obligation to maintain minimum margin requirements, which are crucial to manage the risks associated with borrowed money. In contrast, futures trading demands the posting of an initial margin, which is typically a fraction of the contract's total value. This initial margin serves as a form of security for the contract, enabling traders to speculate on future price movements of a wide array of assets.
The potential returns in both margin and futures trading are significantly influenced by market dynamics and the level of leverage used. Margin trading offers high potential returns, as the borrowed funds can amplify gains (and losses). The leverage in margin trading can enhance profits from favorable crypto movements but also magnifies losses if the market moves against the trader. On the other hand, futures trading can yield considerable returns based on broader market movements. Futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future price of assets, offering the potential for substantial gains if predictions are accurate. However, it's imperative to understand the associated costs in each trading method. Margin trading incurs interest costs, which can accumulate over time, affecting the net return. Futures trading, while not involving borrowing costs, does entail contract fees, which need to be factored into the overall investment strategy. These financial considerations are vital in choosing the right trading approach for one's investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Investment Strategy: Deciding between Margin Trading and Futures Trading
When considering an investment strategy, the decision between margin trading and futures trading hinges on several factors. Margin trading is typically preferred for short-term strategies due to its nature of borrowing funds to amplify potential gains or losses on investments. This approach is particularly suited for investors looking to capitalize on short-term market movements. On the other hand, futures contracts offer flexibility for both short and long-term strategies. This characteristic of futures trading makes it a versatile tool for different investment horizons.
Another significant consideration is the diversification strategy and hedging needs. Margin trading, which allows investors to increase their exposure to specific crypto, can be an effective tool for amplifying investments in particular market segments. However, this comes with a heightened level of risk and requires a solid understanding of the market. In contrast, futures trading can offer broader diversification across different asset classes, making it a more suitable option for investors seeking to spread their risk across various sectors. Additionally, for those whose strategy includes hedging, futures trading presents a more structured approach. It allows investors to hedge against market movements or to balance out other investment positions. Ultimately, choosing between margin and futures trading should be grounded in a comprehensive understanding of each method’s complexities, alignment with individual financial objectives, and a calculated acceptance of the risks involved.
Conclusion
The decision between margin and futures trading is a significant one that requires a thoughtful assessment of your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy. Both approaches offer unique opportunities and challenges, with margin trading providing leverage on a more micro scale in the crypto market and futures trading offering a broader market perspective with structured risk management. While margin trading can be appealing for its potential for high short-term returns, it carries the risk of margin calls and substantial losses. Futures trading, on the other hand, offers a more predictable risk profile but demands a comprehensive understanding of market trends and economic indicators. Ultimately, your choice should align with your overall investment objectives, considering factors such as capital requirements, potential returns, cost implications, and how these strategies fit into your portfolio's diversification and hedging needs. Remember, both margin and futures trading require a nuanced understanding of market dynamics and a disciplined approach to risk management. The right choice is one that not only aligns with your investment goals but also fits comfortably within your risk-bearing capacity.
FAQ About Crypto Futures vs Margin Trading
Q: What are the differences between margins and futures?
A: Margin trading involves borrowing funds to increase buying power and potential returns on investments in assets like cryptocurrencies. It's primarily used for short-term positions and is highly susceptible to market volatility. Futures trading, in contrast, involves buying or selling a financial contract to speculate on the future price of an asset. It's typically used for longer-term positions and includes set terms like specific prices and dates.
Q: Why would anyone trade using margin instead of futures?
A: Traders opt for margin trading over futures for its flexibility and the potential for high short-term gains. Margin trading allows traders to quickly capitalize on market movements and is ideal for those with a deep understanding of specific markets. It's preferred by those seeking to leverage small price movements in the short term.
Q: Which is safer margin or futures?
A: Safety in trading depends on various factors, including market knowledge, risk management strategies, and individual risk tolerance. Margin trading can be riskier due to the possibility of margin calls and the potential to lose more than your initial investment. Futures trading, while also risky, offers more predictable risk due to predefined contract terms. However, the concept of 'safer' is relative and depends on how well the trader understands and manages the risks associated with each method.
Q: Is margin trading better than futures?
A: Whether margin trading is better than futures trading depends on the trader's goals, experience, and risk tolerance. Margin trading is suited for those looking for short-term, high-leverage trades and who are comfortable with the risk of significant losses. Futures trading is better for those looking for a structured approach to speculate or hedge on future prices over a longer term. There's no one-size-fits-all answer; it's about what aligns best with the individual trader's strategy and comfort level with risk.
The information on this website is for general information only. It should not be taken as constituting professional advice from FameEX.