What Are Bitcoin Inscriptions and How Do They Work?
2023-12-26 09:29:26Key Takeaways:
Bitcoin Inscription refers to the method of embedding various types of valuable digital content, such as text, images, videos, and audio, on the satoshis via the Ordinals protocol.
Bitcoin inscriptions typically fall into three distinct types: those that are BRC20-based tokens, image-based, and text-based creations.
The popularity of Bitcoin's inscription feature is still in its early stages, yet it holds the potential to enhance Bitcoin's core ecosystem significantly. Beyond serving as a medium of value and a digital collectible, it could evolve into a foundational infrastructure component.
The first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, known as the” Block 0” or "Genesis Block," was created by Satoshi Nakamoto. Being the inaugural block of the very first blockchain, Satoshi chose to manually embed a message within the block.
“The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.”

Source: Times 03/Jan/2009
This message was possibly intended as a sarcastic critique of the traditional financial crisis. This inscription, the world's first Bitcoin Inscription Ordinal, poses a question: Why has there slow development in the Bitcoin ecosystem since this 2009 Inscription, despite the recent surge in Bitcoin Inscription tokens like SATS and RATS in 2023? To answer these questions, we need to first understand what a Bitcoin Inscription is.
What is the Bitcoin Inscription?
The concept of Bitcoin Inscription also referred to as Ordinal Inscription, represents a significant innovation within the Bitcoin ecosystem. It involves embedding various forms of metadata, including text, images, and videos, onto a satoshi, which is the smallest denomination of Bitcoin. This capability allows for a range of data to be permanently associated with each satoshi, resulting in the creation of distinct digital assets. Bitcoin inscriptions are recorded on the blockchain through specific Bitcoin transactions, making them secure and unalterable. These transactions, which include inscriptions and their related metadata, are compiled into blocks and incorporated into the blockchain by miners, similar to standard transactions. The blockchain's decentralized ledger system ensures that these inscriptions are valuable, unique, permanent, and immutable, offering them the same level of unchangeability as all other Bitcoin transactions.
The concept of Bitcoin inscription did not just emerge recently. Beyond the 'Genesis Block,' which was the first Bitcoin inscription document, new features were introduced as a standard in the v0.9.0 release of Bitcoin Core in March 2014. This feature allowed a sender to mark the output as unspendable, signaling to nodes that these outputs could be disregarded and thus not occupy any space in the UTXO set. Additionally, a restriction was implemented, limiting the size of data in an OP_RETURN output to 40 bytes. Then, this limit was later increased to 83 bytes.
In 2014, Counterparty introduced a new concept of creating alternative digital assets on the Bitcoin network. This was achieved by embedding custom data in transactions using the OP_RETURN function. This innovation by Counterparty spurred the growth of related marketplaces and wallets, significantly contributing to the development of the ecosystem. Moreover, Counterparty played a pivotal role in the creation of the most renowned Bitcoin NFT project, the Rare PePe Cards, which debuted in November 2016 as the first NFT for the Bitcoin Network. Although Counterparty's influence has waned, its critical role in introducing NFT culture to the Bitcoin community remains recognized and its platform continues to be utilized.

The Rare Pepe NFTs Projects by the Counterparty
In this discussion, we delve into the concepts of inscriptions and NFTs. Inscriptions on the Bitcoin network enable the creation of unique digital artifacts, akin to NFTs, by embedding custom content directly onto satoshis. These inscriptions do not necessitate the use of a sidechain or a distinct token. However, whether it's an NFT or a BRC20 token, at its core, it represents a type of inscription. Drawing from the definition of a Bitcoin inscription, any digital content—be it text, images, videos, or audio—engraving in the Bitcoin network can be considered an inscription. Some might argue that while NFTs and inscriptions are unique and indivisible, tokens can be split into smaller, equal parts, suggesting a different nature.
However, when viewed from a broader perspective, tokens also possess a unique character. A token comprises a set of information and rules inscribed on the blockchain. This includes but is not limited to, the total quantity of tokens, transaction details, and ownership distribution. At this level, it too is a form of inscription. The token contract, as recorded on the public blockchain through a protocol, is essentially a string of text code as the inscription. Similarly, the essence of an NFT lies in its image, video, or audio code, also recorded on the public blockchain via a protocol, constituting an image-based type of inscription. Therefore, it can also be one kind of NFT with no difference fundamentally.
How Was Bitcoin Inscription Created?
Bitcoin inscriptions are created using a protocol known as Ordinals, which numbers and locates each Satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin individually. This process uses UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) to engrave digital content and validate the transaction, thus completing the inscription's minting. In simpler terms, developers or crypto users employ the Ordinals protocol to engrave tokens, images, or text information on a specific or random Satoshi. This method is used for creating various types of inscriptions, including BRC-20 tokens, Bitcoin NFTs, and text.
Bitcoin ordinals and inscriptions function together to establish a strong and dependable framework. Ordinals serve as a method for linking an inscription to its owner, while inscriptions offer a way to permanently record various data on the blockchain, ensuring its persistence. In unison, they create a network of interconnected information that powers the whole Ordinals ecosystem.
Unlike token creation from the smart contract in the Ethereum network, the Bitcoin network offers several Ordinals marketplaces. These platforms enable even average crypto investors to easily create Bitcoin inscriptions. They work by connecting to the Ordinals protocol, allowing users to customize inscription rules via the platforms. Users can then personalize their inscription information, pay a minting fee, and easily mint their inscription.
Source from Internet
In most Ordinals marketplaces, the minting of Bitcoin inscriptions can be categorized into three types: BRC-20 tokens, image inscriptions, and text inscriptions. Image and text inscriptions can usually be minted in one session. However, minting BRC-20 tokens often requires batching due to single minting limits and block capacity constraints. Moreover, varying gas fees and network congestion levels can lead to unpredictable minting times for BRC-20 tokens which can range from a few hours to several days.
However, once the initial batch of BRC-20 tokens is minted, others can mint additional tokens in the same manner, up to the total number minted. The cost for minting these tokens is essentially the network's gas fee.
BRC-20 tokens that are yet to be minted can initiate minting requests at any time.
For instance, if A wants to mint a BRC-20 token named X Token with a total supply of 100 million and a single minting limit of 1,000 tokens, anyone can initiate the minting of X Token's inscription through the Ordinals marketplace until all 100 million tokens are minted. After that, other investors can only purchase the tokens through transactions in the Ordinals marketplace.
Paying the gas fee to mint potential BRC-20 tokens is an accessible way for average crypto investors to engage in the Bitcoin Inscription space which offers a cost-effective method of joining the Bitcoin inscription ordinal marketplace.
How Does Bitcoin Inscription Work? What is Its Value?
The role of the Ordinals protocol in the Bitcoin ecosystem is similar to Ethereum's smart contracts, though it's still evolving. This protocol has sparked rapid development within Bitcoin, leading to the creation of BRC-20 tokens and Bitcoin NFTs, which are exploring the ecosystem's potential.
Ordinals are unique identifiers assigned to individual satoshis, the smallest division of Bitcoin (BTC), based on the sequence in which they are mined. The concept of ordinals is rooted in ordinal theory, which stipulates that each satoshi in a Bitcoin block is given a consecutive number starting from 0. This system operates at the social layer, separate from the Bitcoin blockchain, and is optional for users to adopt. It traces back to the very first block mined in the bitcoin network. The application of ordinal theory imparts a numismatic, or collectible, value to satoshis. Each satoshi is endowed with a distinct identity, enabling it to be tracked, transferred, and embedded with meaningful data like images, text, or videos through Bitcoin transactions. These transactions, once executed, become a permanent part of the blockchain.
In the early stages of any new development, its value and significance can be hard to see. This was the case with cryptocurrencies when the initial Bitcoin was criticized as a bubble, and Ethereum, despite its thriving ecosystem, faced skepticism due to network congestion and the lack of 'killer apps'. However, as the crypto market continues to innovate with stablecoins, real-world assets (RWAs), security token offerings (STOs), central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and more, the inherent value of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum is becoming more apparent.
Bitcoin Inscriptions tokens are following a similar path. As tokens like SATS, RATS, and ORDI gain hype in the marketplace, more developers and investments are entering the Bitcoin ecosystem to enrich it and enhance its potential value. Currently, Bitcoin inscriptions serve not only as a medium of value and digital collectibles but also promise to enrich Bitcoin's thriving network development and blockchain ecosystem.
Popular Bitcoin Inscriptions in 2024
As the Bitcoin ecosystem continues to evolve, it might be similar to the early stage of Ethereum and its plethora of ERC-20 tokens. This emerging phase in Bitcoin's journey is dotted with both hidden treasures and potential pitfalls. Selecting Bitcoin inscription tokens requires a comprehensive approach and a well-thought-out investment strategy. In the current market landscape, the following BRC-20-based tokens stand out and merit attention:
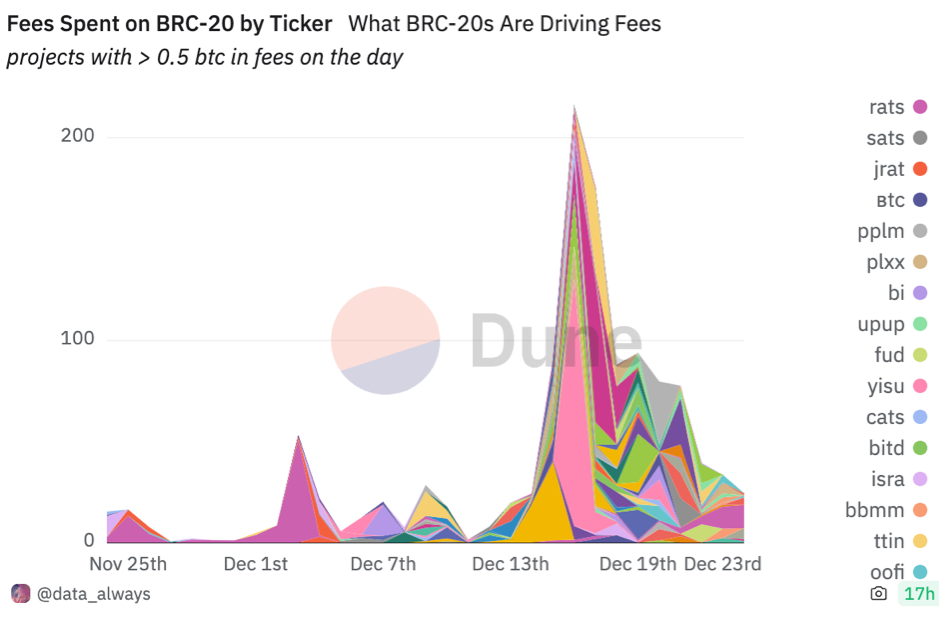
Fees spent on BRC-20, source from Dune
1. ORDI:
ORDI is the first inscription token developed using the Ordinals protocol, serving as the native token of the Ordinals project. As of December 21, 2023, ORDI is priced at $52.51. It has seen a 30-day increase of 132.88% and a 90-day surge of 1,344.62%, positioning it among the top three BRC-20-based tokens with a total market capitalization of $1,101,296,380. The growing adoption of the Ordinals protocol by developers suggests significant potential for ORDI's future growth and development.
2. SATS:
Currently one of the most popular BRC-20-based tokens, SATS is trading at $0.000721 for 1,000 SATS. Initially representing the smallest unit of Bitcoin (Satoshi), SATS aims to become a fundamental element in the crypto payment ecosystem. The SATS project distinguishes itself by diversifying into various business areas, including Bitcoin inscription services, wallets, Bitcoin inscription browsers, and an inscription marketplace. Its practical application across different business sectors makes SATS a notable BRC-20-based token for building a business ecosystem. Read more from our comprehensive research here.
3. RATS:
RATS Token has also gained hype as a new BRC-20-based token with a current price of $0.0003061 and a total market capitalization of $304,274,928. The integration of RATS Token with the Ordinals protocol not only cements its position in the cryptocurrency market but also highlights the vast possibilities at the intersection of blockchain technology and digital creativity. The RATS project's innovative approach and use of blockchain features make it an intriguing asset in the crypto market. However, potential investors should carefully weigh the risks and profits associated with investing in the RATS project. Read more from our comprehensive research here.
Why Should You Care?
The evolving landscape of Bitcoin, marked by the advent of inscriptions, heralds a new era of cultural and technological significance. The increasing attention towards ordinals, inscriptions, and NFTs on the Bitcoin blockchain has sparked various concerns, particularly regarding their potential effects. People are questioning whether the widespread adoption of ordinal theory might affect Bitcoin's fungibility, the implications of a rapid increase in blockchain size, the risks associated with storing illegal content on-chain, and the impact on Lightning Network adoption. This shift is crucial for several reasons and worries:
・Royalty Challenges and Market Trends: Unlike other blockchain platforms, Bitcoin's structure does not inherently support royalties, aligning with the broader NFT market trend towards reduced or non-enforced royalties. This aspect shapes the economic dynamics of the inscription market. The value of inscription-based projects will be determined by various factors such as inscription number, mint uniqueness, art quality, and creator reputation, adding a dynamic aspect to their valuation.
・Uncertain Adoption: Despite the potential, inscription adoption on Bitcoin is not guaranteed. Historical tokenization efforts on Bitcoin have had limited success, and its primary role has been viewed as a non-sovereign monetary network.
・Bitcoin Scaling and Lightning Network: The potential increase in transaction fees due to inscriptions underscores the importance of Bitcoin's scaling solutions, like the Lightning Network. The development of protocols like Taro could shift some NFT activity to Layer 2 solutions in order to enhance the ecosystem's scalability.
・Evolving Use Cases and Adoption: The emergence of inscriptions represents a potential evolution for Bitcoin, driving new use cases, interest, and adoption. This evolution reflects Bitcoin's ongoing transformation in response to technological and cultural shifts.
While definitive answers to these questions are still elusive, they are crucial topics for consideration. A key understanding is that as Bitcoin becomes more popular, competition for block space will intensify, and this space must be paid for, irrespective of whether it's used for inscriptions or regular financial transactions. Importantly, these inscriptions don't bypass existing limitations, nor do they impose additional validation costs on nodes that transmit transactions. The data storage costs remain consistent, whether the block space is occupied by inscriptions or equivalent financial data.
Disclaimer: As with any investment in the cryptocurrency world, it's crucial to conduct thorough research and consider the volatility and risks associated with these assets. FameEX makes no representations on the accuracy or suitability of any official statements made by the exchange regarding the data in this article or any related financial advice.